Generate a Positive-Definite Correlation Matrix for a target Cronbach's alpha.
Constructs a correlation matrix with a specified number of items and target Cronbach's alpha using a constructive one-factor model.
Such a correlation matrix can be applied to the makeScales()
function to generate synthetic data with the predefined alpha.
The algorithm directly builds a positive-definite correlation matrix by solving for item loadings that reproduce the desired average inter-item correlation implied by alpha. Unlike earlier versions of this function, this method guarantees positive definiteness by construction, without post-hoc repair.
Arguments
- items
Integer. Number of items (>= 2).
- alpha
Numeric. Target Cronbach's alpha (0 < alpha < 1).
- variance
Numeric. Controls heterogeneity of item loadings in the underlying one-factor model.
Larger values produce greater dispersion among item loadings, which results in a wider spread of inter-item correlations while preserving the requested Cronbach's alpha.
Typical guidance:
0.05— near-parallel items (very similar correlations)0.10— modest heterogeneity (default)0.15— strong heterogeneity0.20— very strong heterogeneity> 0.25— extreme dispersion; internal shrinkage may occur
For most applied psychometric scales (k < 20), values between
0.05and0.15produce realistic correlation structures.- alpha_noise
Numeric. Controls random variation in the target Cronbach's alpha before the correlation matrix is constructed.
When
alpha_noise = 0(default), the requested alpha is reproduced deterministically (subject to numerical tolerance).When
alpha_noise > 0, a small amount of random variation is added to the requested alpha prior to constructing the matrix. This can be useful in teaching or simulation settings where slightly different reliability values are desired across repeated runs.Internally, noise is added on the Fisher z-transformed scale to ensure the resulting alpha remains within valid bounds (0, 1).
Typical guidance:
0.00— deterministic alpha (default)0.02— very small variation0.05— moderate variation0.10— substantial variation (caution)
Larger values increase the spread of achieved alpha across runs.
- diagnostics
Logical. If
TRUE, returns a list containing the matrix and diagnostic information.
Value
If diagnostics = FALSE, a positive-definite correlation matrix.
If diagnostics = TRUE, a list containing:
R: the correlation matrixdiagnostics: list including achieved alpha, minimum eigenvalue, and internal variance used
Details
The function computes the average inter-item correlation implied by the requested alpha and solves for a one-factor loading structure that reproduces this value. A small adaptive reduction in dispersion may be applied when necessary to ensure a valid positive-definite solution.
The constructive generator assumes a single common factor structure, consistent with typical psychometric scale construction.
Examples
# Example 1
# define parameters
items <- 4
alpha <- 0.85
# apply function
set.seed(42)
cor_matrix <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = items,
alpha = alpha
)
# test function output
print(cor_matrix) |> round(3)
#> item01 item02 item03 item04
#> item01 1.0000000 0.5649919 0.6673592 0.6971190
#> item02 0.5649919 1.0000000 0.4842990 0.5058955
#> item03 0.6673592 0.4842990 1.0000000 0.5975555
#> item04 0.6971190 0.5058955 0.5975555 1.0000000
#> item01 item02 item03 item04
#> item01 1.000 0.565 0.667 0.697
#> item02 0.565 1.000 0.484 0.506
#> item03 0.667 0.484 1.000 0.598
#> item04 0.697 0.506 0.598 1.000
alpha(cor_matrix)
#> [1] 0.8499981
eigenvalues(cor_matrix, 1)
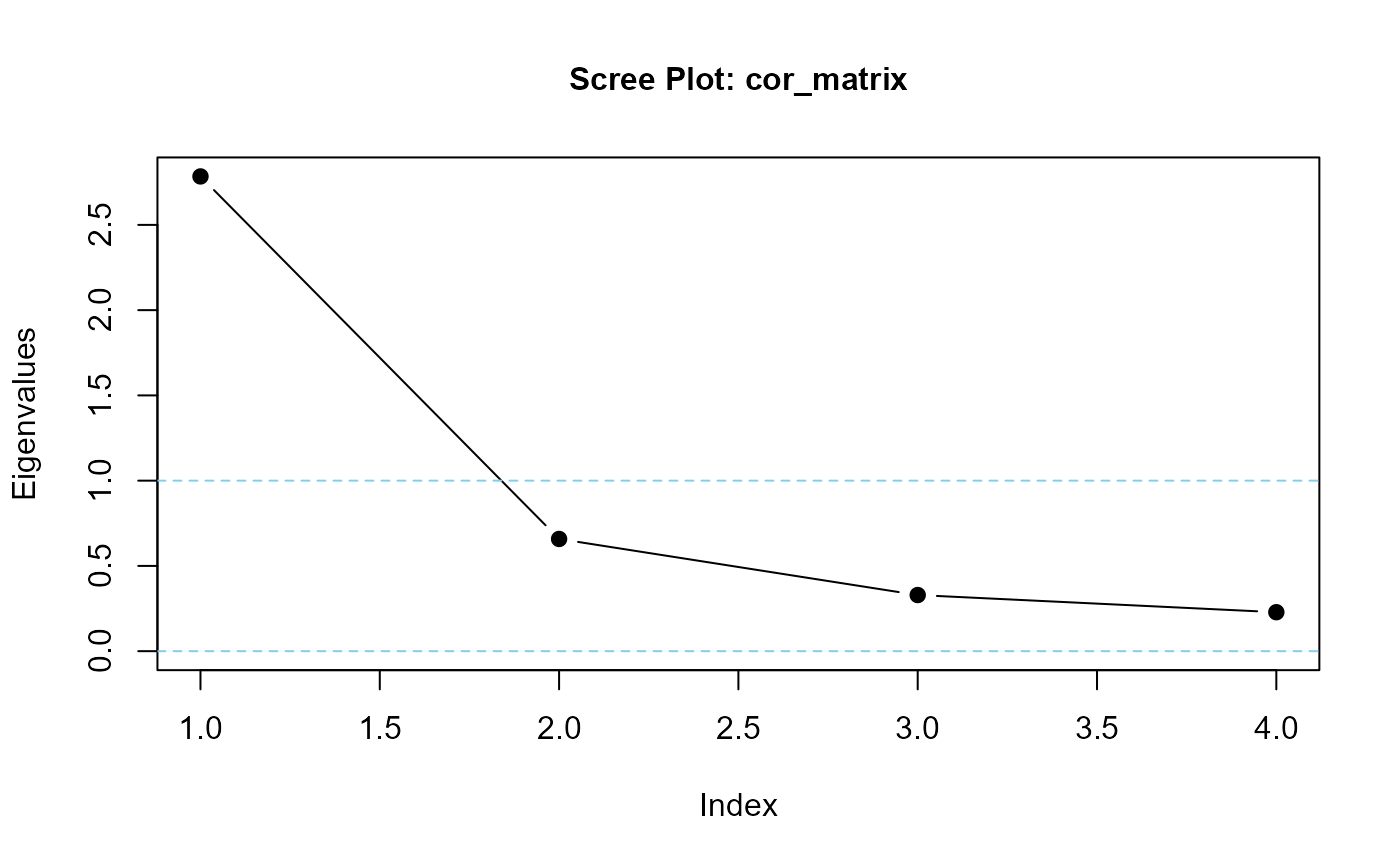 #> cor_matrix is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 2.7665013 0.5480310 0.4036204 0.2818473
# Example 2
# higher alpha, more items, more variability
cor_matrix2 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 8,
alpha = 0.95,
variance = 0.10
)
# test output
cor_matrix2 |> round(2)
#> item01 item02 item03 item04 item05 item06 item07 item08
#> item01 1.00 0.58 0.71 0.58 0.75 0.59 0.69 0.77
#> item02 0.58 1.00 0.66 0.54 0.70 0.55 0.65 0.72
#> item03 0.71 0.66 1.00 0.67 0.86 0.67 0.79 0.88
#> item04 0.58 0.54 0.67 1.00 0.70 0.55 0.65 0.72
#> item05 0.75 0.70 0.86 0.70 1.00 0.71 0.84 0.93
#> item06 0.59 0.55 0.67 0.55 0.71 1.00 0.65 0.73
#> item07 0.69 0.65 0.79 0.65 0.84 0.65 1.00 0.86
#> item08 0.77 0.72 0.88 0.72 0.93 0.73 0.86 1.00
alpha(cor_matrix2) |> round(3)
#> [1] 0.95
eigenvalues(cor_matrix2, 1) |> round(3)
#> cor_matrix is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 2.7665013 0.5480310 0.4036204 0.2818473
# Example 2
# higher alpha, more items, more variability
cor_matrix2 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 8,
alpha = 0.95,
variance = 0.10
)
# test output
cor_matrix2 |> round(2)
#> item01 item02 item03 item04 item05 item06 item07 item08
#> item01 1.00 0.58 0.71 0.58 0.75 0.59 0.69 0.77
#> item02 0.58 1.00 0.66 0.54 0.70 0.55 0.65 0.72
#> item03 0.71 0.66 1.00 0.67 0.86 0.67 0.79 0.88
#> item04 0.58 0.54 0.67 1.00 0.70 0.55 0.65 0.72
#> item05 0.75 0.70 0.86 0.70 1.00 0.71 0.84 0.93
#> item06 0.59 0.55 0.67 0.55 0.71 1.00 0.65 0.73
#> item07 0.69 0.65 0.79 0.65 0.84 0.65 1.00 0.86
#> item08 0.77 0.72 0.88 0.72 0.93 0.73 0.86 1.00
alpha(cor_matrix2) |> round(3)
#> [1] 0.95
eigenvalues(cor_matrix2, 1) |> round(3)
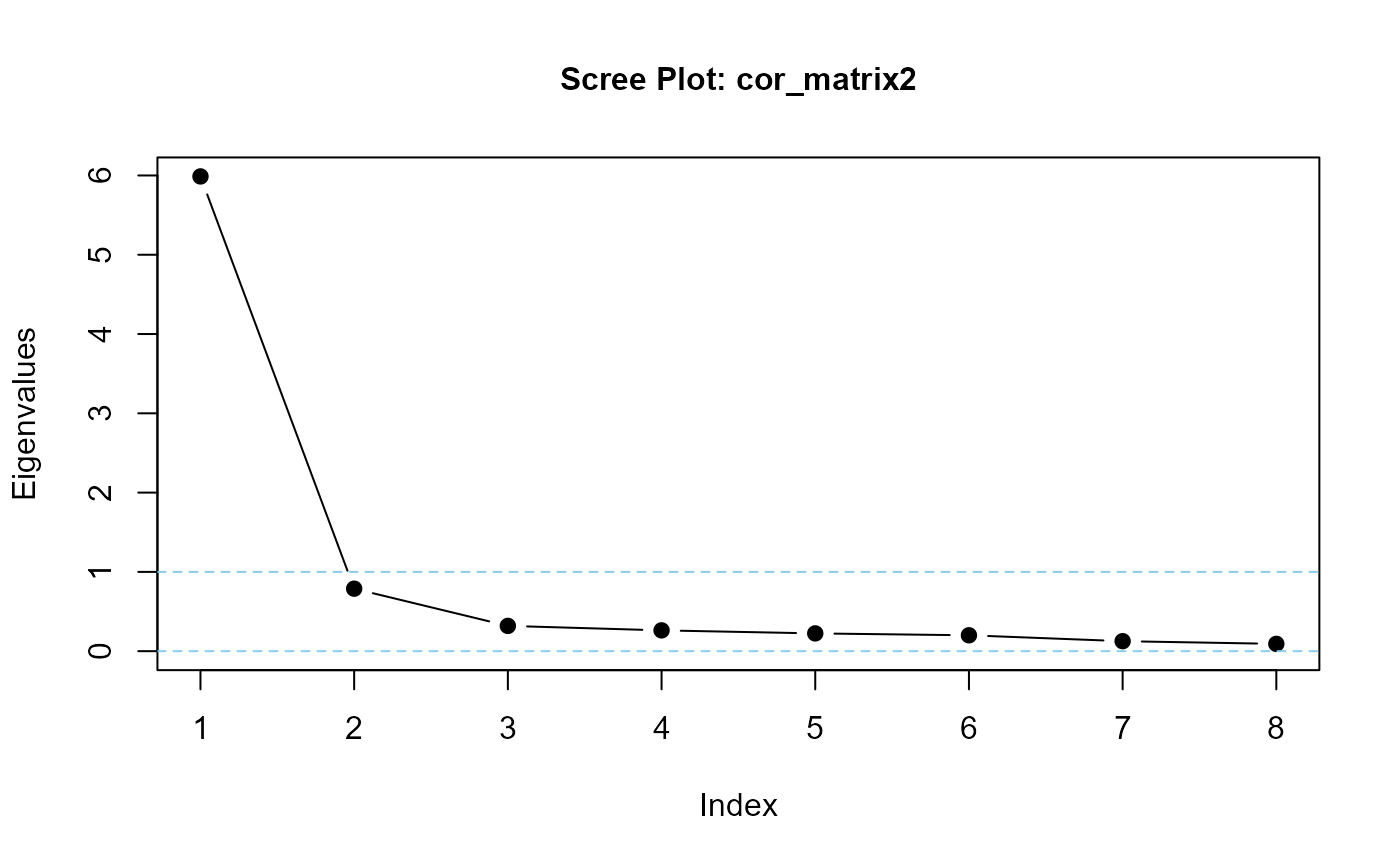 #> cor_matrix2 is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 5.965 0.455 0.452 0.406 0.315 0.209 0.135 0.063
# Example 3
# large random variation around alpha
cor_matrix3 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 6,
alpha = 0.85,
alpha_noise = 0.10
)
# test output
cor_matrix3 |> round(2)
#> item01 item02 item03 item04 item05 item06
#> item01 1.00 0.48 0.51 0.47 0.35 0.36
#> item02 0.48 1.00 0.52 0.48 0.35 0.36
#> item03 0.51 0.52 1.00 0.51 0.38 0.39
#> item04 0.47 0.48 0.51 1.00 0.35 0.36
#> item05 0.35 0.35 0.38 0.35 1.00 0.27
#> item06 0.36 0.36 0.39 0.36 0.27 1.00
alpha(cor_matrix3) |> round(3)
#> [1] 0.807
eigenvalues(cor_matrix3, 1) |> round(3)
#> cor_matrix2 is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 5.965 0.455 0.452 0.406 0.315 0.209 0.135 0.063
# Example 3
# large random variation around alpha
cor_matrix3 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 6,
alpha = 0.85,
alpha_noise = 0.10
)
# test output
cor_matrix3 |> round(2)
#> item01 item02 item03 item04 item05 item06
#> item01 1.00 0.48 0.51 0.47 0.35 0.36
#> item02 0.48 1.00 0.52 0.48 0.35 0.36
#> item03 0.51 0.52 1.00 0.51 0.38 0.39
#> item04 0.47 0.48 0.51 1.00 0.35 0.36
#> item05 0.35 0.35 0.38 0.35 1.00 0.27
#> item06 0.36 0.36 0.39 0.36 0.27 1.00
alpha(cor_matrix3) |> round(3)
#> [1] 0.807
eigenvalues(cor_matrix3, 1) |> round(3)
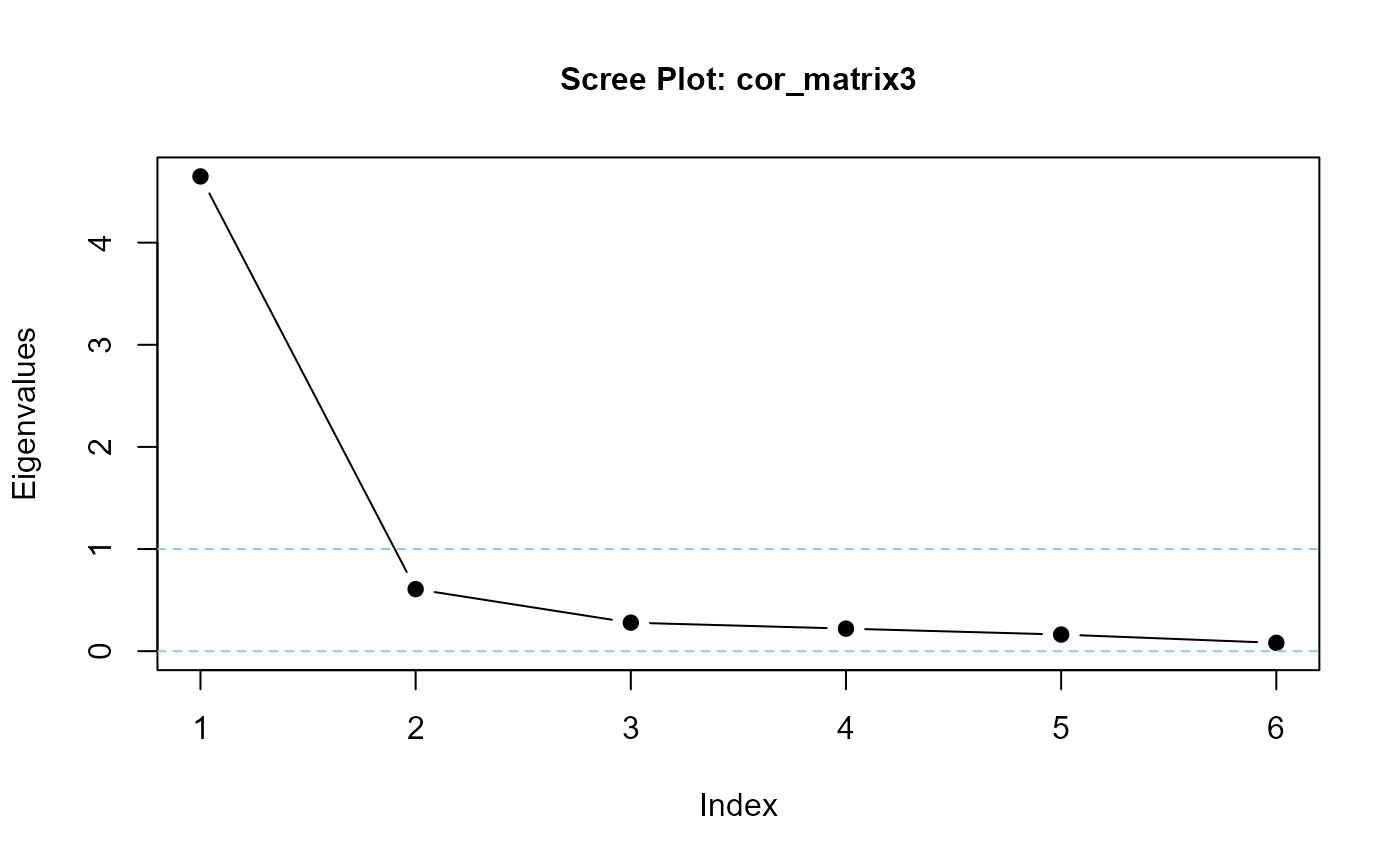 #> cor_matrix3 is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 3.074 0.734 0.680 0.532 0.522 0.458
# Example 4
# with diagnostics
cor_matrix4 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 4,
alpha = 0.80,
diagnostics = TRUE
)
# test output
cor_matrix4
#> $R
#> item01 item02 item03 item04
#> item01 1.0000000 0.5847682 0.4880084 0.5936079
#> item02 0.5847682 1.0000000 0.4126811 0.5019806
#> item03 0.4880084 0.4126811 1.0000000 0.4189194
#> item04 0.5936079 0.5019806 0.4189194 1.0000000
#>
#> $diagnostics
#> $diagnostics$items
#> [1] 4
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_input
#> [1] 0.8
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_target_effective
#> [1] 0.8
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_achieved
#> [1] 0.7999963
#>
#> $diagnostics$average_r
#> [1] 0.4999943
#>
#> $diagnostics$min_eigenvalue
#> [1] 0.3748521
#>
#> $diagnostics$variance_input
#> [1] 0.1
#>
#> $diagnostics$internal_variance_used
#> [1] 0.1
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_noise
#> [1] 0
#>
#>
#> cor_matrix3 is positive-definite
#>
#> [1] 3.074 0.734 0.680 0.532 0.522 0.458
# Example 4
# with diagnostics
cor_matrix4 <- makeCorrAlpha(
items = 4,
alpha = 0.80,
diagnostics = TRUE
)
# test output
cor_matrix4
#> $R
#> item01 item02 item03 item04
#> item01 1.0000000 0.5847682 0.4880084 0.5936079
#> item02 0.5847682 1.0000000 0.4126811 0.5019806
#> item03 0.4880084 0.4126811 1.0000000 0.4189194
#> item04 0.5936079 0.5019806 0.4189194 1.0000000
#>
#> $diagnostics
#> $diagnostics$items
#> [1] 4
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_input
#> [1] 0.8
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_target_effective
#> [1] 0.8
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_achieved
#> [1] 0.7999963
#>
#> $diagnostics$average_r
#> [1] 0.4999943
#>
#> $diagnostics$min_eigenvalue
#> [1] 0.3748521
#>
#> $diagnostics$variance_input
#> [1] 0.1
#>
#> $diagnostics$internal_variance_used
#> [1] 0.1
#>
#> $diagnostics$alpha_noise
#> [1] 0
#>
#>
